Recycling Water: The Role of Graywater Systems in California

What is Graywater and Why Does it Matter?
Graywater refers to the wastewater generated from sinks, showers, and washing machines, excluding toilet waste. Understanding graywater is crucial, especially in a water-scarce state like California, where every drop counts. By recycling graywater, we can significantly reduce the demand on freshwater sources, making it a vital resource for sustainable water management.
Water is the driving force of all nature.
In California, where droughts have become more frequent, utilizing graywater systems can help conserve water for essential uses. This practice not only alleviates the pressure on municipal water supplies but also promotes a more self-sufficient approach to water use in homes. Imagine turning your used shower water into a resource for your garden – that’s the power of graywater!
Moreover, graywater systems can enhance the resilience of our water infrastructure. By reusing water at the household level, we can lessen the strain on treatment plants and reduce the energy costs associated with pumping and treating water. In essence, embracing graywater systems is a win-win for both the environment and our communities.
How Graywater Systems Work: The Basics
Graywater systems are designed to collect, treat, and reuse wastewater from various household sources. Typically, these systems consist of plumbing modifications that direct graywater to storage tanks or filtration units. This technology ensures that water is treated adequately before being reused, making it safe for irrigation or even toilet flushing.
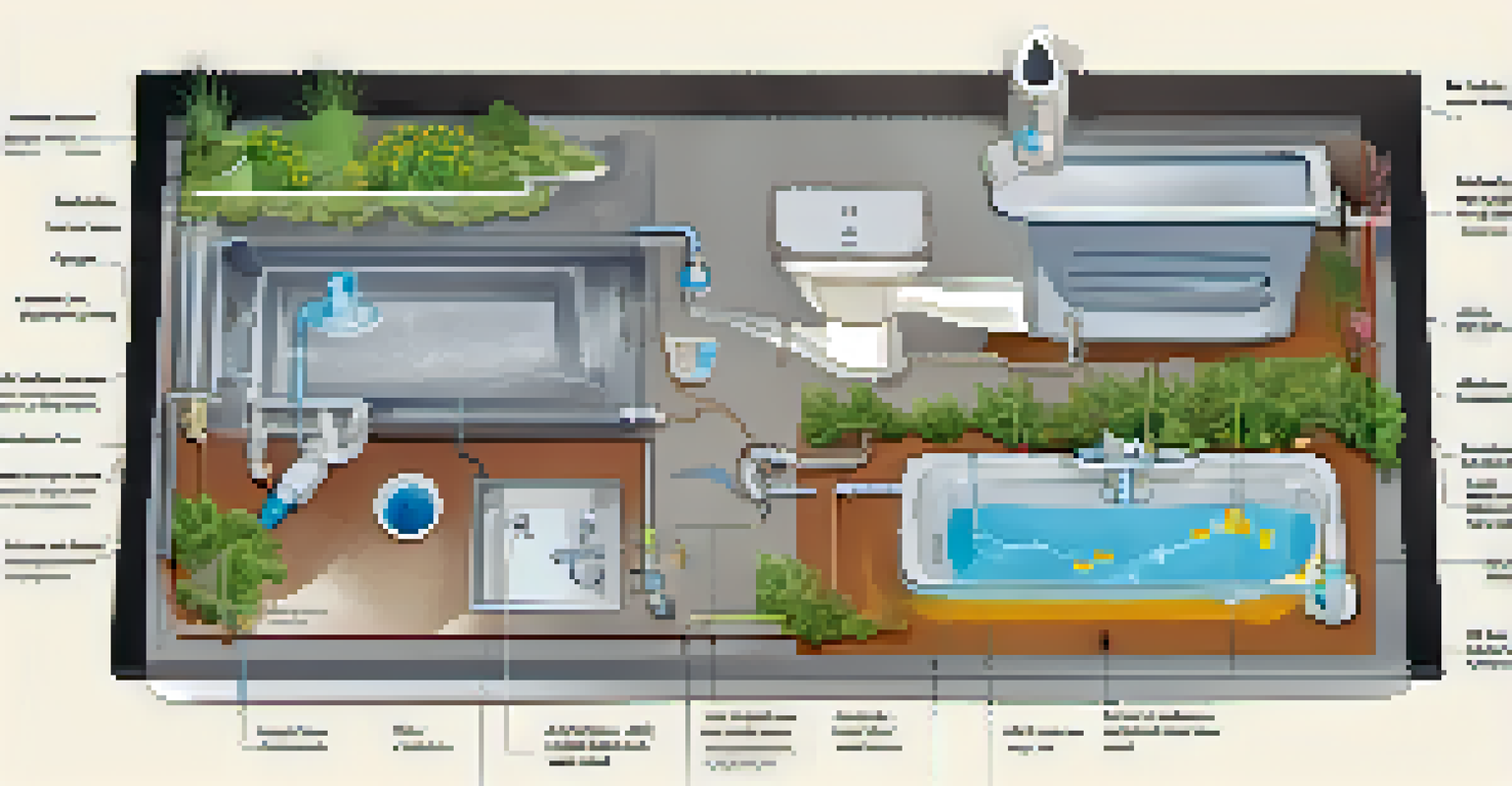
The process often includes simple filtration to remove debris and sometimes more advanced treatment methods, depending on the system. For instance, some systems use biological filters to break down contaminants, ensuring the water is clean enough for reuse. The simplicity and effectiveness of these systems make them accessible to many homeowners looking to conserve water.
Graywater: A Key Resource
Recycling graywater can significantly reduce the demand on freshwater sources, especially in water-scarce regions like California.
It's worth noting that graywater systems can be customized based on individual needs and local regulations. Homeowners can choose from a variety of systems, such as gravity-fed setups or pumped systems, depending on their property layout. This flexibility encourages more people to consider graywater recycling as a viable option.
Benefits of Implementing Graywater Systems
The benefits of graywater systems extend beyond just water conservation. By reusing water, homeowners can see a noticeable reduction in their water bills, making these systems economically appealing. This financial incentive can often justify the initial investment in installing a graywater system.
Conservation is a state of harmony between men and land.
Additionally, using graywater for irrigation can lead to healthier landscapes. Graywater is typically rich in nutrients and organic matter, which can promote plant growth and improve soil health. Picture your garden thriving with less effort, all thanks to the recycling of water that would otherwise go down the drain.
Moreover, graywater systems contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing the amount of wastewater entering sewage treatment plants. This can lessen the ecological impact on local waterways and wildlife, making graywater systems an eco-friendly choice for responsible homeowners.
Regulatory Considerations for Graywater Use
In California, regulations surrounding graywater systems can vary by county, making it essential for homeowners to understand local laws before installation. The state has made efforts to streamline graywater regulations to encourage more residents to adopt these systems. Familiarizing oneself with these guidelines can facilitate a smoother installation process.
Typically, homeowners must adhere to specific requirements regarding system design and maintenance to ensure safety and compliance. For example, certain systems may require permits or inspections, while others might need to follow specific plumbing codes. Understanding these regulations is not just about compliance; it’s about ensuring that the graywater is handled safely.
Cost-Effective Water Conservation
Implementing graywater systems can lead to lower water bills while promoting healthier landscapes through nutrient-rich irrigation.
Many local agencies provide resources and support to help residents navigate these regulations. Engaging with local water conservation programs can also connect homeowners with experts who can guide them through the process. This support can be invaluable in making informed decisions about graywater systems.
Installation Process: What to Expect
Installing a graywater system typically involves several steps, beginning with an assessment of your home’s plumbing. A qualified installer can evaluate which sources of graywater are most suitable for recycling and recommend the best system for your needs. This initial consultation is crucial to ensure that the system integrates seamlessly with your existing setup.
Once the assessment is complete, the actual installation process can vary in complexity. For simpler systems, such as those that reuse water from bathroom sinks or showers, the installation may be relatively quick and straightforward. However, more complex systems might require additional plumbing work and careful planning, which can extend the timeline.
After installation, regular maintenance is key to ensuring the system operates efficiently. Homeowners should familiarize themselves with the maintenance requirements, such as cleaning filters and checking for clogs. With proper care, a graywater system can provide reliable service for years, contributing to sustainable water management.
Common Misconceptions About Graywater Systems
Despite their growing popularity, graywater systems are often surrounded by misconceptions that can deter potential users. One common myth is that graywater is unsafe for plants or gardens, but this is largely untrue. When properly treated, graywater is safe and can actually enhance plant health, providing essential nutrients without the chemicals found in some fertilizers.
Another misconception is that graywater systems are complicated and expensive to install. While there can be costs involved, many systems are designed to be user-friendly and can even save money in the long run through reduced water bills. Additionally, various incentives and rebates are available in California to offset installation costs.
Regulations and Support Available
Understanding local regulations and engaging with community resources can facilitate the safe installation and use of graywater systems.
Finally, some people believe that graywater systems are only suitable for new homes, but that’s far from the truth. Many older homes can also benefit from graywater recycling with proper adjustments. This adaptability makes graywater systems a viable option for a wide range of households.
The Future of Graywater Systems in California
As California continues to face water scarcity challenges, the future of graywater systems looks promising. With increasing awareness of the importance of water conservation, more homeowners are likely to explore graywater recycling as a practical solution. This shift toward sustainable practices aligns with the state’s broader environmental goals.
Innovations in graywater technology are also on the rise, making systems more efficient and easier to use. For instance, new filtration methods and smart monitoring systems are enhancing the safety and effectiveness of graywater reuse. These advancements could pave the way for wider adoption among homeowners seeking to reduce their water footprint.

Moreover, as community initiatives and educational programs promote water conservation, we can expect to see more collaborative efforts in implementing graywater systems. Communities may come together to share resources, knowledge, and support, making graywater recycling a shared responsibility that benefits everyone.