Rainwater Harvesting Techniques for Urban Areas in California

Understanding Rainwater Harvesting and Its Benefits
Rainwater harvesting is the practice of collecting and storing rainwater for reuse. This technique is especially beneficial in urban areas where water scarcity can be a pressing issue. By capturing rainwater, residents can reduce their reliance on municipal water systems and lower their water bills.
Water is the driving force of all nature.
Additionally, rainwater harvesting helps mitigate stormwater runoff, which can lead to flooding and water pollution. By managing rainwater effectively, urban areas can protect local ecosystems and improve water quality in nearby rivers and lakes. This not only benefits the environment but also enhances the overall urban landscape.
In California, where droughts are common, rainwater harvesting can be a crucial strategy for water conservation. Embracing this practice can empower communities to take control of their water resources and promote sustainable living.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems for Urban Areas
There are several types of rainwater harvesting systems that can be implemented in urban settings, ranging from simple to more complex setups. Roof catchment systems are among the most common, where rainwater is collected from rooftops and directed into storage tanks. This method is both efficient and space-saving, making it ideal for urban homes and buildings.
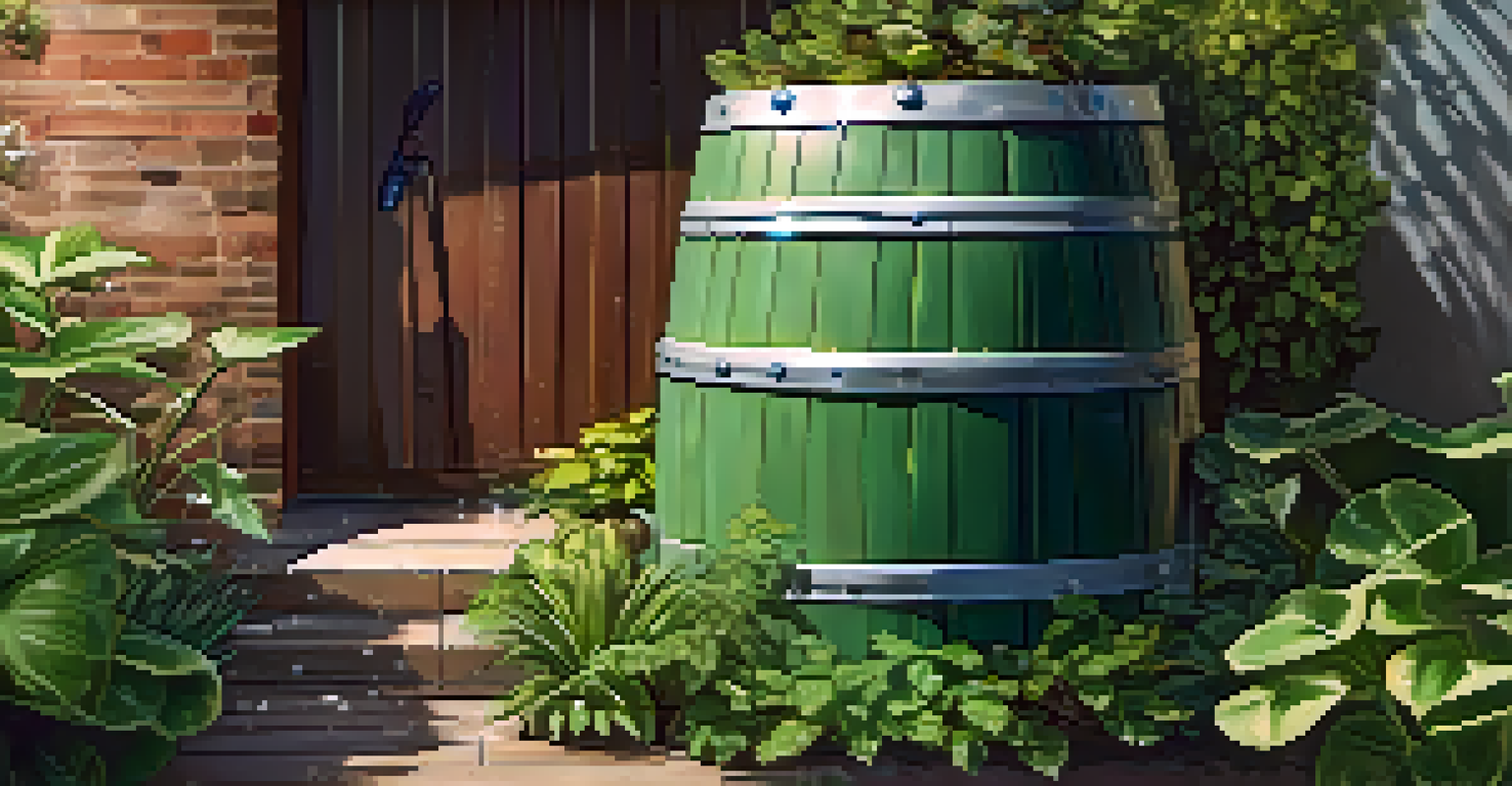

Another popular option is the rain barrel system, which involves placing barrels under downspouts to collect rainwater directly. These barrels can be used for irrigation, cleaning, or even for indoor non-potable uses if properly filtered. This straightforward approach encourages residents to engage in water conservation without requiring significant investment.
Rainwater Harvesting Benefits
Collecting rainwater reduces reliance on municipal systems, mitigates flooding, and promotes sustainable living.
For larger projects, such as community buildings or parks, a cistern system can be installed. Cisterns are larger tanks that store significant amounts of rainwater, providing a more extensive supply for irrigation or other uses. This scalability allows urban areas to tailor their rainwater harvesting systems based on specific needs and available resources.
Designing Your Rainwater Harvesting System
Designing a rainwater harvesting system requires careful planning and consideration of local regulations. Each urban area may have specific guidelines and permits that must be followed, so it's essential to do your research before starting. Local agencies often provide resources to help residents understand these requirements.
We forget that the water cycle and the life cycle are one.
When designing your system, consider factors like roof size, rainfall patterns, and intended water usage. This will help determine the appropriate size of your storage system and filtration needs. For example, a larger roof may collect more rainwater, which means a bigger storage tank will be needed to accommodate the increased volume.
Additionally, think about maintenance and accessibility. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure your system functions efficiently, so plan for easy access to components like filters and storage tanks. This attention to detail will enhance the longevity and effectiveness of your rainwater harvesting system.
Choosing the Right Storage Solutions
Selecting the right storage solution is a key component of effective rainwater harvesting. Storage options range from simple rain barrels to larger cisterns made from materials like plastic, concrete, or fiberglass. Each material has its pros and cons, so it's essential to weigh these factors based on your budget and space availability.
Rain barrels are often the go-to choice for homeowners due to their affordability and ease of installation. They come in various sizes and can often be made from recycled materials, making them an eco-friendly option. However, for those with higher demand or larger properties, investing in a cistern may be more appropriate.
Types of Harvesting Systems
Various rainwater harvesting systems, like roof catchment and rain barrels, cater to different urban needs and spaces.
Whatever storage solution you choose, ensure it is properly covered to prevent contamination and mosquito breeding. Additionally, consider incorporating a first-flush diverter, which helps discard the initial dirty runoff from the roof before clean rainwater enters the storage tank.
Filtering and Treating Collected Rainwater
To ensure the collected rainwater is safe for use, proper filtration and treatment are essential. First, a screening system should be in place to remove debris like leaves and twigs from the water before it enters storage. This prevents clogs and maintains the quality of the collected rainwater.
For those planning to use rainwater for non-potable purposes, additional filtration steps may be necessary. Simple sediment filters can remove larger particles, while activated carbon filters can help eliminate odors and improve taste for applications like irrigation. Understanding your intended use will guide you in selecting the right filtration system.
If you aim to use harvested rainwater for potable purposes, it’s crucial to invest in a more comprehensive treatment system. This may include UV sterilization or reverse osmosis to eliminate pathogens. While this adds to the upfront cost, the long-term savings and sustainability benefits make it a worthy investment.
Utilizing Harvested Rainwater: Practical Applications
Once you have your rainwater harvesting system set up, the next step is to consider how you'll use the collected water. One of the most common applications is for landscape irrigation, which can significantly reduce reliance on municipal water. Using rainwater in your garden not only helps conserve water but also supports healthier plant growth due to its natural quality.
Rainwater can also be used for washing vehicles or outdoor equipment. This practice not only saves water but also reduces the demand on your home's plumbing system. Plus, many people find that rainwater is gentler on surfaces, making it a preferred choice for cleaning.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures the efficiency and longevity of your rainwater harvesting system, maximizing its benefits.
For those interested in more innovative uses, harvested rainwater can even be utilized for toilet flushing if properly treated. This application can lead to substantial water savings, especially in households where toilets account for a significant portion of water usage. Exploring these diverse applications can help maximize the benefits of your rainwater harvesting system.
Maintaining Your Rainwater Harvesting System
Regular maintenance is the key to keeping your rainwater harvesting system in top condition. This includes cleaning gutters and filters to prevent blockages and ensuring that storage tanks are free of algae and debris. A well-maintained system not only performs better but also lasts longer.
It's also essential to check for leaks or signs of wear in pipes and connections. Addressing these issues promptly can help you avoid costly repairs down the road and ensure that your system operates efficiently. Consider scheduling routine inspections, especially before and after rainy seasons.
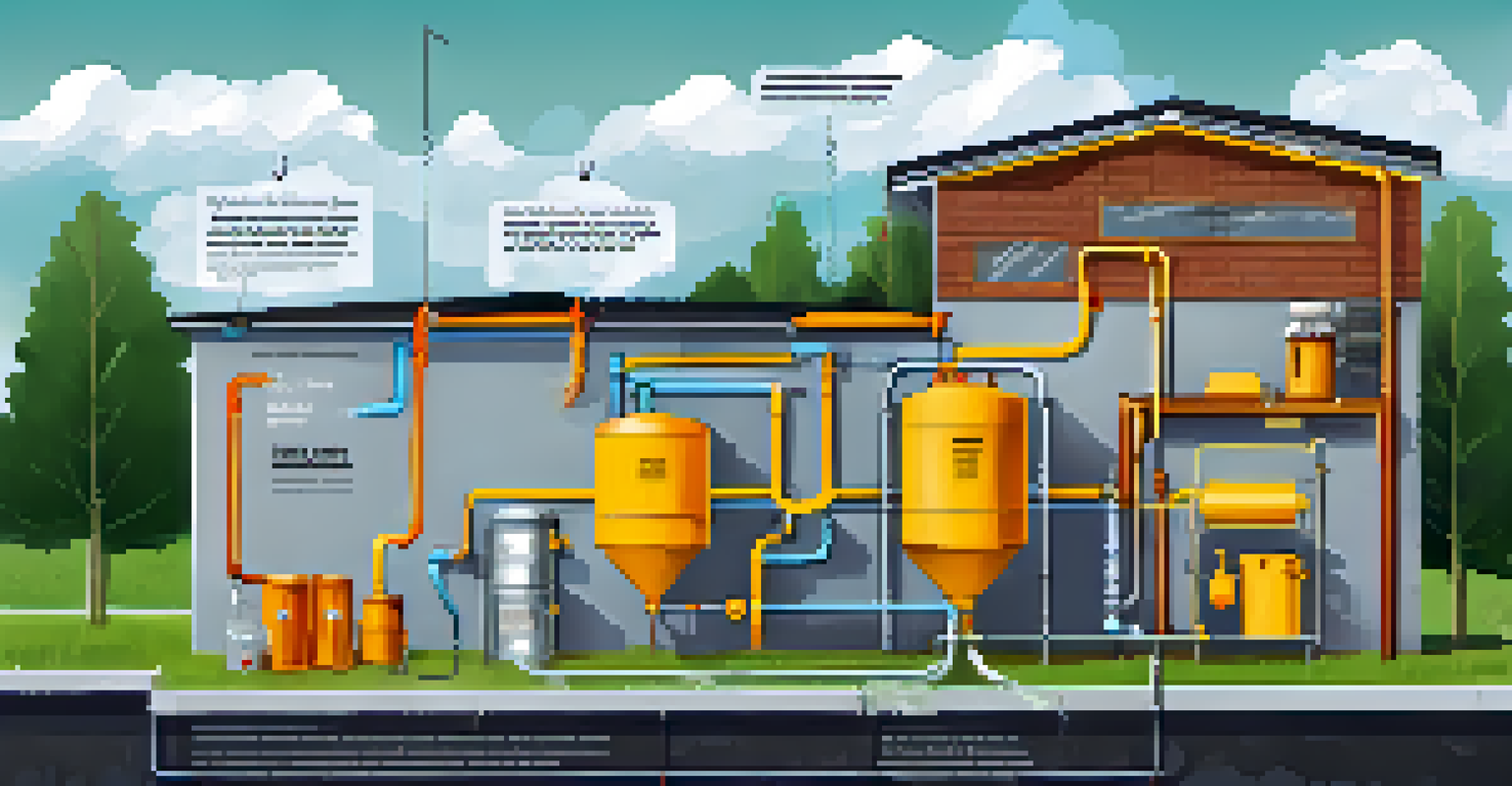
Lastly, keep an eye on the quality of the water being collected. If you notice changes in color, odor, or clarity, it may indicate a problem that needs to be addressed. By staying proactive with maintenance, you can enjoy the full benefits of your rainwater harvesting system while contributing to a more sustainable urban environment.